IOC的引入
1.没有IOC时的情况
创建工程,目录结构如下(spring-framework-introduction只是一个空工程,用于存放接下来会创建的所有项目):

使用原生Servlet构建MVC三层架构
Tomcat配置

POM文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.feliks</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-00-introduction</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.2</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
<encoding>UTF-8</encoding>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>三层架构(MVC)

Controller层
DemoServlet1
package com.feliks.architecture.a_original.servlet;
import com.feliks.architecture.a_original.service.DemoService;
import com.feliks.architecture.a_original.service.impl.DemoServiceImpl;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/demo1")
public class DemoServlet1 extends HttpServlet {
DemoService demoService = new DemoServiceImpl();
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// resp.getWriter().println("DemoServlet1 is running!!!");
resp.getWriter().println(demoService.findAll());
}
}DAO层
DemoDao
package com.feliks.architecture.a_original.dao;
import java.util.List;
public interface DemoDao {
List<String> findAll();
}BeanFactory
package com.feliks.architecture.a_original.dao;
import com.feliks.architecture.a_original.dao.impl.DemoOracleDao;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
/**
* BeanFactory该类强依赖于DemoDaoImpl(紧耦合)
* 怎么解决紧耦合?添加try-catch
*
* 概念:弱依赖
* 使用反射后,错误现象不在出现在编译器中,而是在工程启动之后,如果没有DemoDaoImpl该类,BeanFactory无法构造
* 就会抛出ClassNotFoundException的异常,这样BeanFactory对DemoDaoImpl的依赖程度就降低了,也可当成弱依赖
*
* 硬编码:由于类的全限定名是写死在BeanFactory中的,导致我们每次如果要切换数据库都要重新编译工程才能正常运行
* 优化:在src/main/resource目录下添加factory.properties文件,给每个类名都起一个小名
*/
public class BeanFactory {
// 缓存区,保存已经创建好的对象
private static Map<String, Object> beanMap = new HashMap<>();
// 解析.properties文件
private static Properties properties;
static {
properties = new Properties();
try {
properties.load(BeanFactory.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("factory.properties"));
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new ExceptionInInitializerError("BeanFactory initialize error, cause: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
// public static DemoDao getDemoDao() {
//// return new DemoOracleDao();
// String beanName = null;
// try {
// Class<?> beanClazz = Class.forName(properties.getProperty("demoDao"));
// beanName = beanClazz.getName();
// return (DemoDao) beanClazz.newInstance();
//// return (DemoDao) Class.forName("com.feliks.architecture.a_original.dao.impl.DemoDaoImpl").newInstance();
// } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// throw new RuntimeException("BeanFactory have not [" + beanName + "] bean!", e);
// } catch (IllegalAccessException | InstantiationException e) {
// throw new RuntimeException("[" + beanName + "] instantiation error!", e);
// }
// }
// 引入缓存后我们需要对该方法控制线程并发,引入双检锁保证对象只有一个
/**
* 干脆变成通用的算了,BeanFactory就从配置文件中找对应的全限定类名,反射构造对象返回
* @param beanName
* @return
*/
public static Object getBean(String beanName) {
// 双检锁保证beanMap中确实没有beanName对应的对象
if (!beanMap.containsKey(beanName)) {
synchronized (BeanFactory.class) {
if (!beanMap.containsKey(beanName)) {
try {
Class<?> beanClazz = Class.forName(properties.getProperty(beanName));
Object bean = beanClazz.newInstance();
beanMap.put(beanName, bean);
// return beanClazz.newInstance();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("BeanFactory have not [" + beanName + "] bean!", e);
} catch (IllegalAccessException | InstantiationException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("[" + beanName + "] instantiation error!", e);
}
}
}
}
return beanMap.get(beanName);
}
}
DaoImpl包下
DemoDaoImpl
package com.feliks.architecture.a_original.dao.impl;
import com.feliks.architecture.a_original.dao.DemoDao;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 如果删除该文件就会导致直接报错
*/
public class DemoDaoImpl implements DemoDao {
@Override
public List<String> findAll() {
return Arrays.asList("aaa", "bbb", "ccc");
}
}DemoOracleDao
package com.feliks.architecture.a_original.dao.impl;
import com.feliks.architecture.a_original.dao.DemoDao;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class DemoOracleDao implements DemoDao {
@Override
public List<String> findAll() {
return Arrays.asList("oracle", "oracle", "oracle");
}
}Service层
DemoService
package com.feliks.architecture.a_original.service;
import java.util.List;
public interface DemoService {
List<String> findAll();
}ServiceImpl包
DemoServiceImpl
package com.feliks.architecture.a_original.service.impl;
import com.feliks.architecture.a_original.dao.BeanFactory;
import com.feliks.architecture.a_original.dao.DemoDao;
import com.feliks.architecture.a_original.dao.impl.DemoDaoImpl;
import com.feliks.architecture.a_original.service.DemoService;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class DemoServiceImpl implements DemoService {
// private DemoDao demoDao = new DemoDaoImpl();
// private DemoDao demoDao = BeanFactory.getDemoDao();
/**
* 因为通过配置文件来获取,ServiceImpl中就不需要调用getDao方法了,而是专用getBean方法
* 并指定需要获取的指定名称的类的对象
* 这下我们发现一件事:可以把所有想抽取出来的组件都可以做成外部化配置了
*
* 对于这种会变化的配置、属性等,通常不会直接硬编码在源代码中,而是抽取为一些配置文件的形式(properties、yml、xml、json等),
* 配合程序对配置文件的加载和解析,从而达到动态配置、降低配置耦合的目的
*/
private DemoDao demoDao = (DemoDao) BeanFactory.getBean("demoDao");
public DemoServiceImpl() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
// 这样会创建10个内存地址都不同的DemoDaoImpl
// 于是我们引入缓存的概念
System.out.println(BeanFactory.getBean("demoDao"));
}
}
@Override
public List<String> findAll() {
return demoDao.findAll();
}
}2.(重点)IOC思想的引入
private DemoDao demoDao = new DemoDaoImpl();
private DemoDao demoDao = (DemoDao) BeanFactory.getBean("demoDao");对比两种写法不难发现,前者强依赖/紧耦合,在编译器就必须保证DemoDaoImpl必须存在,后者弱依赖/松耦合,只有到运行期反射创建才知道DemoDaoImpl存在
前者的写法主动声明了DemoDao的实现类,只要编译通过,运行一定没错,后者没有指定实现类,而是由工厂BeanFactory去帮我们找到一个name为demoDao的对象,如果facrtory.properties中生声明的全限定类型出现错误,则会出现强转失败的异常ClassCastException
如果我们使用后者,将对象的创建交给工厂,将控制权交给别人的思想,就可以称为控制反转(Inverse Of Control,IOC)而工厂BeanFactory根据指定beanName去获取和创建对象的过程称为依赖查找(Dependency Lookup,DL)
SpringFramework概述&IOC的依赖查找
关于SpringFramework:Spring Framework官网
The Spring Framework provides a comprehensive programming and configuration model for modern Java-based enterprise applications - on any kind of deployment platform.
A key element of Spring is infrastructural support at the application level: Spring focuses on the “plumbing” of enterprise applications so that teams can focus on application-level business logic, without unnecessary ties to specific deployment environments.
Spring Framework 为现代基于 Java 的企业应用程序提供了一个全面的编程和配置模型 - 在任何类型的部署平台上。
Spring 的一个关键要素是应用程序级别的基础设施支持:Spring 专注于企业应用程序的“管道”,以便团队可以专注于应用程序级别的业务逻辑,而无需与特定部署环境进行不必要的联系。
- 任何类型的部署平台:无论是操作系统还是Web容器(Tomcat等)都是可以部署基于SpringFramework的应用的
- 企业应用程序:包含JavaSE和JavaEE在内,其被称为一站式解决方案
- 编程和配置模型:基于框架编程,以及基于框架进行功能和组件的配置
- 基础框架支持:SpringFramework不含任何业务功能,它只是一个底层的应用抽象支持
- 脚手架:使用它可以更加快速的构建应用
1.官方文档
Spring Framework Overview :: Spring Framework
Spring makes it easy to create Java enterprise applications. It provides everything you need to embrace the Java language in an enterprise environment, with support for Groovy and Kotlin as alternative languages on the JVM, and with the flexibility to create many kinds of architectures depending on an application’s needs.
Spring 使创建 Java 企业应用程序变得容易。它为您提供了一切 需要在企业环境中采用 Java 语言,并支持 Groovy 和 Kotlin 作为 JVM 上的替代语言,并具有创建许多 架构的种类取决于应用程序的需求。
SpringFramework是一个分层的、JavaSE/JavaEE的一站式轻量级开源框架,以IOC和AOP为内核,并提供表现层、持久层、业务层等领域的解决方案,同时还提供了整合第三方开源技术的能力
IOC & AOP:SpringFramework的两大和新特性:Inverse Of Control控制反转、Aspect Oriented Programming面向切面编程- 轻量级:对比于重量级框架,其规模更小,消耗的资源更小
- 一站式:覆盖企业级开发中的所有领域
- 第三方整合:SpringFreamework可以很方便的整合进其他的第三方技术(例如持久层MyBatis/Hibernate,表现层框架Struts2,权限校验框架Shiro等)
- 容器:SpringFramework的底层有一个管理对象和组建的容器,由它来支撑基于SpringFramework构建的应用的运行
2.概述SpringFramework
SpringFramework是一个开源的、松耦合的、分层的、可配置的一站式企业级Java开发框架,它的核心是IOC和AOP,它可以更容易地构建出企业级Java应用,并且它可以根据应用开发的组件需要整合对应的技术
3.为什么使用SpringFramework
- IOC:组件之间的解耦
- AOP:切面编程可以将应用业务做统一或特定的功能增强,能实现应用业务与增强逻辑的解耦
- 容器与事件:管理应用中使用的组件Bean、托管Bean的生命周期、事件与监听器的驱动机制
- 方便Web、事务控制、测试与其他技术的整合
4.SpringFramework包含的模块
- beans、core、context、expression【核心包】
- aop【切面编程】
- jdbc【整合jdbc】
- orm【整合ORM框架】
- tx【事务控制】
- web【Web层技术】
5.IOC-DL依赖查找


5.1 引入依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.feliks</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-01-ioc</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>6.1.4</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>5.2 创建配置文件
官网:XML Schemas :: Spring Framework

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- bean definitions here -->
<bean id="person" class="com.feliks.spring.basic_dl.a_quickstart_byname.bean.Person"/>
</beans>5.3 创建基本类和启动类
Person
package com.feliks.spring.basic_dl.a_quickstart_byname.bean;
public class Person {
}QuickstartByNameApplication
package com.feliks.spring.basic_dl.a_quickstart_byname;
import com.feliks.spring.basic_dl.a_quickstart_byname.bean.Person;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class QuickstartByNameApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BeanFactory factory = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("basic_dl/quickstart-byname.xml");
Person person = (Person) factory.getBean("person");
System.out.println(person);
}
}- 选用
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext加载配置文件,使用BeanFactory接口来接收(体现了多态的思想,BeanFactory是顶层接口)
运行main方法打印Person的全限定类名+内存地址

以上就是SpringFramework中IOC依赖查找的实现
IOC的依赖查找&依赖注入
1.依赖查找DL
1.1 byName如上章
1.2 byType
目录结构:

quickstart-byname.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- bean definitions here -->
<bean class="com.feliks.spring.basic_dl.b_bytype.bean.Person"/>
</beans>不声明id属性
启动类
package com.feliks.spring.basic_dl.b_bytype;
import com.feliks.spring.basic_dl.b_bytype.bean.Person;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class QuickstartByTypeApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BeanFactory factory = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("basic_dl/quickstart-bytype.xml");
Person person = factory.getBean(Person.class);
System.out.println(person);
}
}
因为使用bytype的方式创建Bean实例,向getBean方法传入了Person类的Class类型,所以不需要强转
运行结果

打印Person类的全限定名
1.3 接口与实现类
目录结构

DemoDao
package com.feliks.spring.basic_dl.b_bytype.dao;
import java.util.List;
public interface DemoDao {
public List<String> findAll();
}DemoDaoImpl
package com.feliks.spring.basic_dl.b_bytype.dao.impl;
import com.feliks.spring.basic_dl.b_bytype.dao.DemoDao;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class DemoDaoImpl implements DemoDao {
@Override
public List<String> findAll() {
return Arrays.asList("aaa", "bbb", "ccc");
}
}在quickstart-bytype.xml中加入DemoDaoImpl的声明
<bean class="com.feliks.spring.basic_dl.b_bytype.dao.impl.DemoDaoImpl"/>启动类添加从BeanFactory中取出DemoDao,并调用里面的findAll()方法
package com.feliks.spring.basic_dl.b_bytype;
import com.feliks.spring.basic_dl.b_bytype.bean.Person;
import com.feliks.spring.basic_dl.b_bytype.dao.DemoDao;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class QuickstartByTypeApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BeanFactory factory = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("basic_dl/quickstart-bytype.xml");
Person person = factory.getBean(Person.class);
System.out.println(person);
DemoDao demoDao = factory.getBean(DemoDao.class);
System.out.println(demoDao.findAll());
}
}运行结果

可以看到DemoDaoImpl成功注入并且调用了finalAll()方法,由此也可知BeanFactory可以根据接口的类型找到对应的实现类
2.依赖注入DI
以上创建的实例是不带属性的,如果要创建的bean带预设值的属性,就是IOC的另外一种实现了,称为依赖注入,交给IOC容器让它帮我们找到和赋值
2.1 简单属性值注入
目录结构

2.1.1 配置文件&声明类
Person
package com.feliks.spring.basic_di.a_quickstart_set;
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
}Cat
package com.feliks.spring.basic_di.a_quickstart_set;
public class Cat {
private String name;
private Person master;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Cat{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", master=" + master +
'}';
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Person getMaster() {
return master;
}
public void setMaster(Person master) {
this.master = master;
}
}resources下basic_di的配置文件
inject-set.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="person" class="com.feliks.spring.basic_di.a_quickstart_set.Person"/>
<bean id="cat" class="com.feliks.spring.basic_di.a_quickstart_set.Cat"/>
</beans>2.1.2 启动类
QuickstartInjectBySetXmlApplication
package com.feliks.spring.basic_di.a_quickstart_set;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class QuickstartInjectBySetXmlApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BeanFactory beanFactory = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("basic_di/inject-set.xml");
Person person = beanFactory.getBean(Person.class);
System.out.println(person);
Cat cat = beanFactory.getBean(Cat.class);
System.out.println(cat);
}
}运行结果

2.1.3 对Person赋值
在<bean>标签下使用property标签赋值
<bean id="person" class="com.feliks.spring.basic_di.a_quickstart_set.Person">
<property name="name" value="test-person-bytest"/>
<property name="age" value="18"/>
</bean>
保存,启动!

2.2 关联Bean赋值
<bean id="cat" class="com.feliks.spring.basic_di.a_quickstart_set.Cat">
<property name="name" value="test-cat"/>
<!-- ref引用上面的person对象 -->
<property name="master" ref="person"/>
</bean>对于赋值类型是别的bean,如上的master类型是person,需要对其声明另一个属性:ref,表示要关联赋值的bean的id
保存后重新启动

3.依赖查找和依赖注入的对比
- 作用目标不同
- 依赖查找的作用目标可以是方法体内,也可以是方法体外
- 依赖注入的作用目标通常是类成员
- 实现方式不同
- 依赖查找通常主动使用上下文搜索
- 依赖注入通常借助一个上下文被动的接收
IOC的依赖查找高级&BeanFactory&ApplicationContext
目录结构

1.依赖查找(DL)的多种方式
1.1 ofType
创建oftype包测试查找方式
项目结构

创建配置类,声明Bean
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- bean definitions here -->
<bean id="demoMySQLDao" class="com.feliks.spring.basic_dl.c_oftype.dao.impl.DemoMySQLDao"/>
<bean id="demoOracleDao" class="com.feliks.spring.basic_dl.c_oftype.dao.impl.DemoOracleDao"/>
<bean id="demoPostgreDao" class="com.feliks.spring.basic_dl.c_oftype.dao.impl.DemoPostgreDao"/>
</beans>修改启动类,在获取bean的时候尝试一次性取出多个Bean
将BeanFactory接口换成ApplicationContext
package com.feliks.spring.basic_dl.c_oftype;
import com.feliks.spring.basic_dl.c_oftype.dao.DemoDao;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import java.util.Map;
public class OfTypeApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("basic_dl/quickstart-oftype.xml");
Map<String, DemoDao> beans = ctx.getBeansOfType(DemoDao.class);
beans.forEach((beanName, bean) -> {
System.out.println(beanName + " : " + bean.toString());
});
}
}传入一个接口类型,跟之前依赖查找一样自动帮我们找到该接口下的实现类
启动!

为什么要用ApplcationContext接口而不是BeanFactory?
2.BeanFactory & ApplicationContext?
ApplicationContext也是一个接口,且通过接口继承关系可知其是BeanFactory的子接口
public interface ApplicationContext extends EnvironmentCapable, ListableBeanFactory, HierarchicalBeanFactory, MessageSource, ApplicationEventPublisher, ResourcePatternResolver {
...
}2.1 官方文档
The
org.springframework.beansandorg.springframework.contextpackages are the basis for Spring Framework’s IoC container. TheBeanFactoryinterface provides an advanced configuration mechanism capable of managing any type of object.ApplicationContextis a sub-interface ofBeanFactory. It adds:
- Easier integration with Spring’s AOP features
- Message resource handling (for use in internationalization)
- Event publication
- Application-layer specific contexts such as the
WebApplicationContextfor use in web applications.
org.springframework.beans和org.springframework.context包是 SpringFramework 的 IOC 容器的基础。BeanFactory接口提供了一种高级配置机制,能够管理任何类型的对象。ApplicationContext是BeanFactory的子接口。它增加了:
- 与 SpringFramework 的 AOP 功能轻松集成
- 消息资源处理(用于国际化)
- 事件发布
- 应用层特定的上下文,例如 Web 应用程序中使用的
WebApplicationContext
You should use an
ApplicationContextunless you have a good reason for not doing so, withGenericApplicationContextand its subclassAnnotationConfigApplicationContextas the common implementations for custom bootstrapping. These are the primary entry points to Spring’s core container for all common purposes: loading of configuration files, triggering a classpath scan, programmatically registering bean definitions and annotated classes, and (as of 5.0) registering functional bean definitions.你应该使用
ApplicationContext,除非能有充分的理由解释不需要的原因。一般情况下,我们推荐将GenericApplicationContext及其子类AnnotationConfigApplicationContext作为自定义引导的常见实现。这些实现类是用于所有常见目的的 SpringFramework 核心容器的主要入口点:加载配置文件,触发类路径扫描,编程式注册 Bean 定义和带注解的类,以及(从5.0版本开始)注册功能性 Bean 的定义。
| Feature | BeanFactory |
ApplicationContext |
|---|---|---|
| Bean instantiation/wiring——Bean的实例化和属性注入 | Yes | Yes |
| Integrated lifecycle management——声明周期管理 | No | Yes |
Automatic registrationBeanPostProcessor——Bean后置处理器的支持 |
No | Yes |
Automatic registrationBeanFactoryPostProcessor——BeanFactory后置处理器的支持 |
No | Yes |
Convenient access (for internationalization)MessageSource——消息转换服务(国际化) |
No | Yes |
Built-in publication mechanismApplicationEvent——事件发布机制(事件驱动) |
No | Yes |
2.2 BeanFactory与ApplicationContext的对比
BeanFactory接口提供了一个抽象的配置和对象的管理机制,ApplicationContext是BeanFactory的子接口,它简化了AOP的整合、消息机制、事件机制以及对Web环境的扩展(WebApplicationContext等),BeanFacory是没有这些扩展的
ApplicationContext主要扩展了:
- AOP的支持(
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator作用于Bean的初始化之后) - 配置元信息(
BeanDefinition、Environment、注解等) - 资源管理(
Resource抽象) - 事件驱动机制(
ApplicationEvent、ApplicationListener) - 消息与国际化(
LocaleResolver) Environment抽象(SpringFramework 3.1 以后)
3.依赖查找
3.1 withAnnotation
IOC容器除了可以根据一个父类/接口来找实现类,还可以根据类上标注的注解来找到对应的Bean
3.1.1 声明Bean+直接+配置文件

@Color
package com.feliks.spring.basic_dl.d_withanno;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface Color {
}
在Black与Red类上标注@Color注解
Black
package com.feliks.spring.basic_dl.d_withanno.bean;
import com.feliks.spring.basic_dl.d_withanno.anno.Color;
@Color
public class Black {
}Red
package com.feliks.spring.basic_dl.d_withanno.bean;
import com.feliks.spring.basic_dl.d_withanno.anno.Color;
@Color
public class Red {
}
Dog
package com.feliks.spring.basic_dl.d_withanno.bean;
public class Dog {
}
配置文件 quickstart-withanno
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- bean definitions here -->
<bean id="black" class="com.feliks.spring.basic_dl.d_withanno.bean.Black"/>
<bean id="red" class="com.feliks.spring.basic_dl.d_withanno.bean.Red"/>
<bean id="dog" class="com.feliks.spring.basic_dl.d_withanno.bean.Dog"/>
</beans>3.1.2 启动类
使用getBeansWithAnnotation()方法
package com.feliks.spring.basic_dl.d_withanno;
import com.feliks.spring.basic_dl.d_withanno.anno.Color;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import java.util.Map;
public class WithAnnoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("basic_dl/quickstart-withanno.xml");
Map<String, Object> beans = ctx.getBeansWithAnnotation(Color.class);
beans.forEach((beanName, bean) -> {
System.out.println(beanName + " : " + bean.toString());
});
}
}运行结果

可以看到成功取出了bean
3.2 获取IOC容器中的所有Bean
通过ApplicationContext的getBeanDefinitionNames()方法取出IOC容器中的所有bean
package com.feliks.spring.basic_dl.d_withanno.bean;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
public class BeannamesApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("basic_dl/quickstart-withanno.xml");
String[] beanNames = ctx.getBeanDefinitionNames();
Stream.of(beanNames).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}运行结果

4.依赖查找高级使用——延迟查找
对于一些特殊的场景,需要依赖容器中某些特定的Bean,但是当他们不存在时也能使用默认/缺省策略来处理逻辑,此时如果只是单纯的使用try-catch手动new一个对象会很不优雅,如4.1
4.1 实现Bean缺失时的缺省加载
目录结构

quickstart-lazylookup中只定义Cat类的bean,不定义Dog
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- bean definitions here -->
<bean id="cat" class="com.feliks.spring.basic_dl.d_withanno.bean.Cat"/>
</beans>ImmediatlyLookupApplication
package com.feliks.spring.basic_dl.d_withanno.bean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class ImmediatlyLookupApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("basic_dl/quickstart-lazylookup.xml");
Cat cat = ctx.getBean(Cat.class);
System.out.println(cat);
Dog dog;
try {
dog = ctx.getBean(Dog.class);
} catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException e) {
dog = new Dog();
}
System.out.println(dog);
}
}运行结果

根据以上方法不难发现,如果我们对于每一个Bean都这样操作,工作量将会非常大,必须对其进行优化
4.2 优化-获取bean前先检查
ApplicationContext中的containsBean方法可以专门用来检查容器中是否存在指定的Bean
// containsBean只能传bean的id
Dog dog = ctx.containsBean("dog") ? (Dog) ctx.getBean("dog") : new Dog();- 该方法不能传类型
4.3 再优化-延迟查找
在ApplicationContext中有一个方法叫getBeanProvider,如果我们直接getBean,而容器中找不到对应的bean就会报NoSuchBeanDefinitionException,而使用getBeanProvider运行main方法后不会报错,只有当我们调用dogProvider的getObject时,真正要取出包装里面的Bean时才会报异常,这也就实现了延后Bean的获取时机,延后了异常可能出现的时机
/**
* 在SpringFramework4.3中引入了一个新的API:ObjectProvider可以实现延迟查找
* 当我们想获取一个Bean的时候可以先不报错,先让我们拿着,当我们要使用的时候再拆开决定里面有没有
*/
ObjectProvider<Dog> dogProvider = ctx.getBeanProvider(Dog.class);4.4 延迟查找-ObjectProvider
ObjectProvider中还有一个方法getIfAvailable(),它可以在找不到Bean时返回null而不抛出异常
Dog dog = dogProvider.getIfAvailable();
if (dog == null) {
dog = new Dog();
}4.5 更优雅的ObjectProvider
Dog dog = dogProvider.getIfAvailable(() -> new Dog());Dog dog = dogProvider.getIfAvailable(Dog::new);在一般情况下取出的Bean都会马上或者间歇地用到,ObjectProvider还提供了一个ifAvailable()方法,可以在Bean存在时执行Consumer接口的方法
dogProvider.ifAvailable(dog -> System.out.println(dog));注解驱动IOC与组件扫描
1.注解驱动的IOC容器
在xml驱动的IOC容器中,我们使用的是ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("basic_dl/quickstart-lazylookup.xml");而使用注解驱动的IOC容器,使用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
目录结构

1.1 注解驱动IOC的依赖查找(DL)
Person
package com.feliks.spring.annotation.bean;
public class Person {
}1.1.1 配置类与Bean注册
QuickstartConfiguration
package com.feliks.spring.annotation.configuration;
import com.feliks.spring.annotation.bean.Person;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* 对比于xml文件作为驱动,注解驱动需要的是配置类,一个配置类就可以
* 类似的理解为一个xml配置文件,配置类没有特殊的限制,只需要标注上@Configuration注解即可
*/
@Configuration
public class QuickstartConfiguration {
/**
* 一个person方法,返回一个Person对象,标注上@Bean注解后就可以解释为
* 向IOC容器中注册一个类型为Person,id为person的Bean,方法的返回值代表注册的类型
* 方法名代表Bean的id,也可以直接在@Bean注解内显式声明Bean的id,只不过不叫id而是name
*
* @return
*/
@Bean(name = "aaa")
public Person person() {
return new Person();
}
}
在xml中如果要进行依赖查找需要通过<bean>标签
<bean id="person" class="com.feliks.spring.basic_dl.a_quickstart_byname.bean.Person"/>而使用注解进行依赖查找需要使用@Bean注解
1.1.2 启动类初始化注解IOC容器
AnnotationConfigApplication
package com.feliks.spring.annotation;
import com.feliks.spring.annotation.bean.Person;
import com.feliks.spring.annotation.configuration.QuickstartConfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class AnnotationConfigApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(QuickstartConfiguration.class);
Person person = ctx.getBean(Person.class);
System.out.println(person);
}
}运行结果

可以看到在配置类中的Bean确实被打印出来
1.2 注解驱动IOC的依赖注入
创建对象后先不返回,通过set方法把属性set进去再返回就完成了依赖注入
@Bean
public Person person() {
Person person = new Person();
person.setName("person");
person.setAge(123);
return person;
}相当于
<bean id="person" class="com.feliks.spring.annotation.bean.Person">
<property name="name" value="person"/>
<property name="age" value="123"/>
</bean>Cat类里面注入Person类型的属性
@Bean
public Cat cat() {
Cat cat = new Cat();
cat.setName("test-cat-anno");
cat.setPerson(person());
return cat;
}相当于
<bean id="cat" class="com.feliks.spring.annotation.bean.Cat">
<property name="name" value="test-cat"/>
<property name="master" ref="person"/>
</bean>2.组件注册与组件扫描(重点)
使用上方的声明方式,如果需要注册的bean、组件特别多,那编写@Bean很明显加大了很多工作量,于是SpringFramework有可供我们用来快速注册组件的注解,模式注解(stereotype annotation)
2.1 @Component
在类上标注@Component注解,代表该类会被当作一个Bean注册到IOC容器中
@Component
public class Person {
}相当于xml中的
<bean class="com.feliks.spring.basic_dl.a_quickstart_byname.bean.Person"/>如果要指定Bean的名称(就是xml中的id),直接在@Component中声明value属性即可
@Component(value = "aaa")
public class Person {
}如果不指定Bean的名称,它默认的规则是类的首字母小写,例如Person的默认名称就是person,DepartmentServiceImpl的默认名称就是departmentServiceImpl
2.2 组件扫描
只声明组件,如果写配置类的时候还是写@Configuration注解,直接启动IOC容器,其实容器是无法感知到有@Component的存在的,一定会报NoSuchBeanDefinitionException
2.2.1 @ComponentScan
在配置类上额外标注一个@ComponentScan注解,指定其要扫描的路径,他就能够扫描指定路径的包以及包下所有的@Component组件
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.feliks.spring.annotation.c_scan.bean")
public class ComponentScanConfiguration {
}比较老版本的写法会在路径前写上basePackages
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.feliks.spring.annotation.c_scan.bean")
public class ComponentScanConfiguration {
}
Person类注解上@Component
@Component
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
}启动类
public class AnnotationConfigApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(QuickstartConfiguration.class);
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ComponentScanConfiguration.class);
Person person = ctx.getBean(Person.class);
System.out.println(person);
}
}运行结果

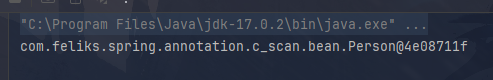
Person确实被扫到了
2.2.2 不使用@ComponentScan的组件扫描
不写@ComponentScan就需要用到AnnotationConfigApplicationContext的一个为String类型的可变形参构造器
public class AnnotationConfigApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext("com.feliks.spring.annotation.c_scan.bean");
Person person = ctx.getBean(Person.class);
System.out.println(person);
}
}
2.2.3 xml中启用组件扫描
除了使用注解驱动IOC组件扫描,也可以使用xml来驱动IOC启动组件扫描
quickstart-componentscan.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- bean definitions here -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.feliks.spring.annotation.c_scan.bean"/>
</beans>启动类
package com.feliks.spring.annotation;
import com.feliks.spring.annotation.c_scan.bean.Person;
import com.feliks.spring.annotation.configuration.ComponentScanConfiguration;
import com.feliks.spring.annotation.configuration.QuickstartConfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class AnnotationConfigApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("basic_dl/quickstart-componentscan.xml");
Person person = ctx.getBean(Person.class);
System.out.println(person);
}
}
2.3 组件注册的其他注解
SpringFramework对于Web开发的MVC三层架构,它额外提供了三个注解:@Controller、@Service、@Repository,分别代表控制层、业务层、持久层,他们与@Component的作用完全一致,底层其实也是@Component
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface Controller {
@AliasFor(
annotation = Component.class
)
String value() default "";
}
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface Service {
@AliasFor(
annotation = Component.class
)
String value() default "";
}
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface Repository {
@AliasFor(
annotation = Component.class
)
String value() default "";
}这三个注解在进行符合三层架构开发时,对于那些ServiceImpl实现类,就可以直接标注@Service注解而不用一个个写bean标签或者是@Bean注解了
2.4 @Configuration也是@Component
如果上面指定的扫描包中去掉后面的bean,让它扫描整个根包
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.feliks.spring.annotation.c_scan")
public class ComponentScanConfiguration {
}启动类
public class AnnotationConfigApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ComponentScanConfiguration.class);
String[] beanDefinitionNames = ctx.getBeanDefinitionNames();
Stream.of(beanDefinitionNames).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}运行结果

可以发现配置类componentScanConfiguration也被注册到IOC容器中了
来看看@Configuration注解
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface Configuration {
@AliasFor(
annotation = Component.class
)
String value() default "";
boolean proxyBeanMethods() default true;
boolean enforceUniqueMethods() default true;
}它也被标注了@Component注解,确实作为bean,被注册到了IOC容器中
3.注解驱动与xml驱动
3.1 xml引入注解
xml中引入注解配置,需要开启注解配置<context:annotation-config/>

@Configuration
public class AnnotationConfigConfiguration {
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- bean definitions here -->
<context:annotation-config/>
<bean class="com.feliks.spring.annotation.d_importxml.config.AnnotationConfigConfiguration"/>
</beans>3.2 注解引入xml
在注解配置中引入xml,需要在配置类上标注@ImportResource注解,并声明配置文件的路径
@Configuration
@ImportResource("classpath:annotation/beans.xml")
public class ImportXmlAnnotationConfiguration {
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- bean definitions here -->
<bean id="person" class="com.feliks.spring.annotation.c_scan.bean.Person"/>
</beans>依赖注入-属性注入&SpEL表达式
1.setter属性注入


1.1 xml方式的setter注入
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="person" class="com.feliks.spring.basic_di.a_quickstart_set.Person">
<property name="name" value="test-person-bytest"/>
<property name="age" value="18"/>
</bean>
<bean id="cat" class="com.feliks.spring.basic_di.a_quickstart_set.Cat">
<property name="name" value="test-cat"/>
<property name="master" ref="person"/>
</bean>
</beans>1.2 注解方式的setter注入
Person
package com.feliks.spring.basic_di.a_quickstart_set;
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
}Cat
package com.feliks.spring.basic_di.a_quickstart_set;
public class Cat {
private String name;
private Person master;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Cat{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", master=" + master +
'}';
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Person getMaster() {
return master;
}
public void setMaster(Person master) {
this.master = master;
}
}2.构造器注入
有一些bean的属性依赖需要在调用构造器的时候就设置好,或者是一些bean的实体类本身没有无参构造器,此时就要使用构造器注入了
2.1 修改Bean


Person
package com.feliks.spring.basic_di.b_constructor.bean;
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public Person(String name, Integer age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
}inject-constructor
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean name="person" class="com.feliks.spring.basic_di.b_constructor.bean.Person">
<property name="name" value="teste-person-byconstructor"/>
<property name="age" value="18"/>
</bean>
</beans>启动类
package com.feliks.spring.basic_di.b_constructor;
import com.feliks.spring.basic_di.b_constructor.bean.Person;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class QuickstartInjectByConstructorApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("basic_di/inject-constructor.xml");
Person person = ctx.getBean(Person.class);
System.out.println(person);
}
}运行结果会报错
Caused by: java.lang.NoSuchMethodException: com.feliks.spring.basic_di.b_constructor.bean.Person.<init>()
at java.base/java.lang.Class.getConstructor0(Class.java:3585)
at java.base/java.lang.Class.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.java:2754)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.SimpleInstantiationStrategy.instantiate(SimpleInstantiationStrategy.java:80)
... 14 more2.2 xml方式的构造器注入
在<bean>标签的内部,可以声明一个子标签constructor-arg用来指定构造器中的属性
<bean name="person" class="com.feliks.spring.basic_di.b_constructor.bean.Person">
<constructor-arg index="0" name="name" value="test-person-constructor"/>
<constructor-arg index="1" name="age" value="18"/>
</bean>启动启动类
public class QuickstartInjectByConstructorApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("basic_di/inject-constructor.xml");
Person person = ctx.getBean(Person.class);
System.out.println(person);
System.out.println("Name: " + person.getName() + "\nAge: " + person.getAge());
}
}
看到注入的属性成功被打印出来
2.3 注解方式的构造器注入

新建配置类并在里面配置@Bean注解
package com.feliks.spring.basic_di.b_constructor.config;
import com.feliks.spring.basic_di.b_constructor.bean.Person;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class InjectByAnnotationConfig {
@Bean
public Person person() {
return new Person("test-person-annotation-byconstructor", 18);
}
}启动类
public class QuickstartInjectByConstructorApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(InjectByAnnotationConfig.class);
Person person = ctx.getBean(Person.class);
System.out.println(person);
System.out.println("Name: " + person.getName() + "\nAge: " + person.getAge());
}
}运行结果

确实是我们用注解式构造器注入的属性
3.注解式属性注入
注册bean的方式除了有@Bean注解的方式还有组件扫描,声明式注册好的组件属性值该怎么处理?
3.1 @Component下的属性注入

属性注入方式:@Value
Black
实现注解式属性注入,可以直接在要注入的字段上标注上@Value注解
package com.feliks.spring.basic_di.c_value_spel.bean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Black {
@Value("black-value-annotation")
private String name;
@Value("0")
private Integer order;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Black{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", order=" + order +
'}';
}
}InjectValueAnnotationApplication
package com.feliks.spring.basic_di.c_value_spel;
import com.feliks.spring.basic_di.c_value_spel.bean.Black;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class InjectValueAnnotationApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext("com.feliks.spring.basic_di.c_value_spel.bean");
Black black = ctx.getBean(Black.class);
System.out.println(black);
}
}运行结果

3.2 外部配置文件引入-@PropertySource
如果要在SpringFramework中使用properties文件怎么办?
3.2.1 创建Bean+配置文件

Red(别忘了写@Component注解将类注册到IOC容器中)
对于properties类型的属性,@Value需要使用占位符来代表注入的属性,跟jsp中的el表达式一致
package com.feliks.spring.basic_di.c_value_spel.bean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Red {
@Value("${red.name}")
private String name;
@Value("${red.order}")
private Integer order;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Red{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", order=" + order +
'}';
}
}red.properties
red.name = red-value-by-properties
red.order = 13.2.2 配置类中引入配置文件
InjectValueConfiguration
package com.feliks.spring.basic_di.c_value_spel.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.feliks.spring.basic_di.c_value_spel.bean")
@PropertySource("classpath:basic_di/value/red.properties")
public class InjectValueConfiguration {
}启动类
package com.feliks.spring.basic_di.c_value_spel;
import com.feliks.spring.basic_di.c_value_spel.bean.Red;
import com.feliks.spring.basic_di.c_value_spel.config.InjectValueConfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class InjectValueAnnotationApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(InjectValueConfiguration.class);
Red red = ctx.getBean(Red.class);
System.out.println(red);
}
}运行结果

在properties中写入的属性成功注入并被打印
3.2.3 xml中使用占位符

在xml中,占位符的使用方式与@Value是一模一样的
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:basic_di/value/red.properties"/>
<bean class="com.feliks.spring.basic_di.c_value_spel.bean.Red">
<property name="name" value="${red.name}"/>
<property name="order" value="${red.order}"/>
</bean>
</beans>在Red类中添加setter方法
package com.feliks.spring.basic_di.c_value_spel.bean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Red {
@Value("${red.name}")
private String name;
@Value("${red.order}")
private Integer order;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Red{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", order=" + order +
'}';
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setOrder(Integer order) {
this.order = order;
}
}启动类
public class InjectValueAnnotationApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("basic_di/inject-spel.xml");
Red red = ctx.getBean(Red.class);
System.out.println(red);
}
}运行结果

3.2.4 占位符的取值范围
作为一个properties文件,其加载到IOC容器后会转换成Map的形式来保存配置,而SpringFramework本身在初始化时就会有一些配置项,他们也都存放在这个Map中,占位符的取值就是从这些配置中读取的
3.3 SpEL表达式
官网:Core Technologies (spring.io)
当我们要在属性注入时用一些特殊的数值,例如一个Bean需要依赖另一个Bean的属性,或者需要动态处理一个特定的属性值,此时占位符${}就没办法处理了,需要使用SpEL表达式
3.3.1 SpEL
Spring Expression Language,本身可以算SpringFramework的组成部分但又可以单独使用,支持调用属性值、属性参数以及方法调用、数组存储、逻辑计算等功能
3.3.2 SpEL属性注入
SpEL的语法统一使用#{}表示,花括号内部编写表达式语言
Blue,提供getter、setter方法,使用@Value注解配合SpEL完成字面量的属性注入
package com.feliks.spring.basic_di.c_value_spel.bean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Blue {
@Value("#{'blue-value-by-spel'}")
private String name;
@Value("#{2}")
private Integer order;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getOrder() {
return order;
}
public void setOrder(Integer order) {
this.order = order;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Blue{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", order=" + order +
'}';
}
}启动类
public class InjectValueAnnotationApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(InjectValueConfiguration.class);
Blue blue = ctx.getBean(Blue.class);
System.out.println(blue);
}
}运行结果

3.3.3 Bean属性引用
SpEL可以取出IOC容器中其他Bean的属性

package com.feliks.spring.basic_di.c_value_spel.bean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Green {
@Value("#{'copy of ' + blue.name}")
private String name;
@Value("#{blue.order + 1}")
private Integer order;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getOrder() {
return order;
}
public void setOrder(Integer order) {
this.order = order;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Green{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", order=" + order +
'}';
}
}运行启动类
package com.feliks.spring.basic_di.c_value_spel;
import com.feliks.spring.basic_di.c_value_spel.bean.Blue;
import com.feliks.spring.basic_di.c_value_spel.bean.Green;
import com.feliks.spring.basic_di.c_value_spel.bean.Red;
import com.feliks.spring.basic_di.c_value_spel.config.InjectValueConfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class InjectValueAnnotationApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(InjectValueConfiguration.class);
Blue blue = ctx.getBean(Blue.class);
System.out.println(blue);
Green green = ctx.getBean(Green.class);
System.out.println(green);
}
}运行结果

可以看到Blue中注入的属性被Green取出来了
xml的方式
在xml中声明Blue和Green的bean,Blue的bean要声明其id,不然在Green的bean中使用SpEL表达式会报错
<bean id="blue" class="com.feliks.spring.basic_di.c_value_spel.bean.Blue">
<property name="name" value="#{'blue-value-by-spel-xml'}"/>
<property name="order" value="#{1}"/>
</bean>
<bean id="green" class="com.feliks.spring.basic_di.c_value_spel.bean.Green">
<property name="name" value="#{'copy of ' + blue.name}"/>
<property name="order" value="#{blue.order + 1}"/>
</bean>启动类
public class InjectValueAnnotationApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("basic_di/inject-spel.xml");
Blue blue = ctx.getBean(Blue.class);
System.out.println(blue);
Green green = ctx.getBean(Green.class);
System.out.println(green);
}
}运行结果

3.3.4 方法调用
SpEL表达式不仅可以引用对象的属性,还可以直接引用类常量,以及调用对象的方法
在White类里面初始化属性name、order,生成getter、setter方法,重写toString方法
name注入blue的name并截取前3个字符,order取Integer的最大值
package com.feliks.spring.basic_di.c_value_spel.bean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class White {
@Value("#{blue.name.substring(0 ,3)}")
private String name;
// 直接引用类的属性,需要在类的全限定名外面使用T()包围
@Value("#{T(java.lang.Integer).MAX_VALUE}")
private Integer order;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getOrder() {
return order;
}
public void setOrder(Integer order) {
this.order = order;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "White{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", order=" + order +
'}';
}
}运行启动类
public class InjectValueAnnotationApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(InjectValueConfiguration.class);
White white = ctx.getBean(White.class);
System.out.println(white);
}
}运行结果

使用xml的方式注入
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:basic_di/value/red.properties"/>
<bean class="com.feliks.spring.basic_di.c_value_spel.bean.Red">
<property name="name" value="${red.name}"/>
<property name="order" value="${red.order}"/>
</bean>
<bean id="blue" class="com.feliks.spring.basic_di.c_value_spel.bean.Blue">
<property name="name" value="#{'blue-value-by-spel-xml'}"/>
<property name="order" value="#{1}"/>
</bean>
<bean id="green" class="com.feliks.spring.basic_di.c_value_spel.bean.Green">
<property name="name" value="#{'copy of ' + blue.name}"/>
<property name="order" value="#{blue.order + 1}"/>
</bean>
<bean id="white" class="com.feliks.spring.basic_di.c_value_spel.bean.White">
<property name="name" value="#{blue.name.substring(0, 3)}"/>
<property name="order" value="#{T(java.lang.Integer).MAX_VALUE}"/>
</bean>
</beans>启动
public class InjectValueAnnotationApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("basic_di/inject-spel.xml");
White white = ctx.getBean(White.class);
System.out.println(white);
}
}运行结果

依赖注入-自动注入&复杂类型注入
1.自动注入
xml中的ref属性可以在一个Bean中注入另一个Bean,注解同样也可以这么干
1.1 @Autowired
在Bean中直接在属性或者setter方法上标注@Autowired注解,IOC容器会按照属性对应的类型从容器中找到对应类型的Bean赋值到对应的属性上,实现自动注入
1.1.1 创建Bean
Person类
package com.feliks.spring.basic_di.d_complexfield.bean;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Person {
private String name = "adminstrator";
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}Dog类
package com.feliks.spring.basic_di.d_complexfield.bean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Dog {
@Value("dogdog")
private String name;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dog{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", person=" + person +
'}';
}
}1.1.2 Dog注入Person的三种方式
方式一
// 方法一
@Autowired
private Person person;方式二
// 方法二
@Autowired
public Dog(Person person) {
this.person = person;
}方式三
// 方法三
@Autowired
public void setPerson(Person person) {
this.person = person;
}1.1.3 启动类测试
把Person和Dog都扫进IOC容器,之后取出Dog并打印
启动类
InjectComplexFieldAnnotationApplication
package com.feliks.spring.basic_di.d_complexfield;
import com.feliks.spring.basic_di.d_complexfield.bean.Dog;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class InjectComplexFieldAnnotationApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext("com.feliks.spring.basic_di.d_complexfield.bean");
Dog dog = ctx.getBean(Dog.class);
System.out.println(dog);
}
}运行结果,可以看到Dog里已经依赖了Person

1.1.4 注入的Bean不存在
将Person上的@Component注解注释掉,让它不注册到IOC容器中
//@Component
public class Person {
private String name = "adminstrator";
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}但同时我们又不想让程序抛出异常,就可以在@Autowired里面加上required = false的属性
// 方法一
@Autowired(required = false)
private Person person;此时运行启动类

就会发现person=null
1.2 @Autowired在配置类的使用、

在配置类中,注册@Bean时也可以标注@Autowired
package com.feliks.spring.basic_di.d_complexfield.config;
import com.feliks.spring.basic_di.d_complexfield.bean.Cat;
import com.feliks.spring.basic_di.d_complexfield.bean.Person;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.feliks.spring.basic_di.d_complexfield.bean")
public class InjectComplexFieldConfiguration {
@Bean
@Autowired
public Cat cat(Person person) {
Cat cat = new Cat();
cat.setName("mimi");
cat.setPerson(person);
return cat;
}
}Person
package com.feliks.spring.basic_di.d_complexfield.bean;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Person {
private String name = "adminstrator";
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}记得把上面注释掉的@Component打开
因为配置类的上下文中没有Person的注册,自然就没有person()方法,就可以使用@Autowired注释来进行自动注入
启动类
public class InjectComplexFieldAnnotationApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(InjectComplexFieldConfiguration.class);
Cat cat = ctx.getBean(Cat.class);
System.out.println(cat);
}
}运行结果

1.3 多个相同类型Bean的自动注入
在Person类上已经声明了一个@Component注解,证明在IOC容器中已经有一个Person的Bean了,然后再在配置类里再注册一个
InjectComplexFieldConfiguration
package com.feliks.spring.basic_di.d_complexfield.config;
import com.feliks.spring.basic_di.d_complexfield.bean.Cat;
import com.feliks.spring.basic_di.d_complexfield.bean.Person;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.feliks.spring.basic_di.d_complexfield.bean")
public class InjectComplexFieldConfiguration {
@Bean
@Autowired
public Cat cat(Person person) {
Cat cat = new Cat();
cat.setName("mimi");
cat.setPerson(person);
return cat;
}
@Bean
public Person master() {
Person master = new Person();
master.setName("master");
return master;
}
}在Person类上面的注解加一个名称
@Component("adminstrator")此时在IOC容器内有两个Person类型的Bean,一个叫master,一个叫administrator
当我们试图运行的时候,控制台会报错:
Caused by: org.springframework.beans.factory.NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException: No qualifying bean of type 'com.feliks.spring.basic_di.d_complexfield.bean.Person'SpringFramework专门针对这种情况提供了两个注解:@Qualifier、@Primary
1.3.1 @Qualifier:指定注入Bean的名称
@Qualifier注解的使用目标是要注入的Bean,它配合@Autowired使用,可以显式地指定要注入哪一个Bean
把上面写的Dog类里定义的Person添加@Qualifier指定要注入对应哪个名字的Person类型的Bean
// 方法一
@Autowired
@Qualifier("administrator")
private Person person;要注意一下的是,记得把配置类里注册的Cat注释掉,因为我们并没有指定让它注册哪个Person的Bean,是依然会报错的
运行启动类
public class InjectComplexFieldAnnotationApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(InjectComplexFieldConfiguration.class);
Dog dog = ctx.getBean(Dog.class);
System.out.println(dog);
}
}运行结果

成功让Dog里面的Person注入到了名为administrator的Person
1.3.2 @Primary:默认Bean
@Primary注解的使用目标是被注入的Bean,在一个应用中,一个类型的Bean注册只能有一个,它配合@Bean使用,可以指定默认注入的Bean
@Bean
@Primary
public Person master() {
Person master = new Person();
master.setName("master");
return master;
}我们之前在Cat中自动注入了一个Person,因为我们没有指明具体要注入的Person的名称,就变成刚刚写了默认的master
package com.feliks.spring.basic_di.d_complexfield.bean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Cat {
@Value("miaomiao")
private String name;
@Autowired
private Person person;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Cat{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", person=" + person +
'}';
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setPerson(Person person) {
this.person = person;
}
}启动类
public class InjectComplexFieldAnnotationApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(InjectComplexFieldConfiguration.class);
Dog dog = ctx.getBean(Dog.class);
System.out.println(dog);
Cat cat = ctx.getBean(Cat.class);
System.out.println(cat);
}
}运行结果

1.3.3 @Autowired注入的原理逻辑
先拿属性对应的类型去IOC容器中找到Bean,如果找到了一个可以直接返回;
如果有多个类型一样的Bean,把属性名拿过去跟这些Bean的id逐个比对,如果有一个相同的,直接返回;
如果没有任何相同的id与要注册的属性名相同,则会抛出NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException异常
1.4 多个相同类型的Bean的全部注入
以上是通过两种不同的方法来注入一个Bean,保证注入的唯一性,但是如果要一下子把所有指定类型的Bean都注入进去应该怎么办?注入一个用单个对象接收,注入一组对象就用集合来接收
@Component
public class Dog {
@Value("dogdog")
private String name;
// 注入一组对象
@Autowired
private List<Person> persons;
// ......
}重新运行启动类就会发现persons对象
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(InjectComplexFieldConfiguration.class);
Dog dog = ctx.getBean(Dog.class);
System.out.println(dog);运行结果

如上就可以一次性把所有的Person都注入进来,通过控制台输出我们可以发现persons里面有两个对象
1.5 @Resource
@Resource也是用来属性注入的注解,它和@Autowired的不同在于:
@Autowired:按照类型注入@Resource:直接按照属性名/Bean的名称注入
@Resource相当于同时标注@Autowired和@Qualifier
新建Bird类,在里面使用@Resource注入Person
package com.feliks.spring.basic_di.d_complexfield.bean;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@Component
public class Bird {
@Resource(name = "master")
private Person person;
}注意,如果没有@Resource注解,要检查pom文件内是否添加了javax.annotation.api的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.annotation</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.annotation-api</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
</dependency>启动类
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(InjectComplexFieldConfiguration.class);
Bird bird = ctx.getBean(Bird.class);
System.out.println(bird);运行结果

1.6 @Inject
@Inject这个注解跟@Autowired一样的策略,按照类型注入
pom文件中导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.inject</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.inject</artifactId>
<version>1</version>
</dependency>在Cat类中注入一个名为superMaster的Person
@Inject
@Named("superMaster")
private Person person;类似于@Autowired和@Qualifier
1.6.1 @Autowired和@Inject的对比
@Inject虽然和@Autowired作用一致,但是因为@Inject属于JSR规范,不会因为不使用SpringFramework而失去意义
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import javax.inject.Inject;1.7 依赖注入的注入方式
| 注入方式 | 被注入成员是否可变 | 是否依赖于IOC框架的API | 使用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 构造器注入 | 不可变 | 否(xml、编程式注入不依赖) | 不可变的固定注入 |
| 参数注入 | 不可变 | 否(高版本中注解配置类中的@Bean方法参数注入可以不标注注解) |
注解配置类中@Bean方法注册bean |
| 属性注入 | 不可变 | 是(只能通过标注注解来侵入式注入) | 通常用于不可变的固定注入 |
| setter注入 | 可变 | 否(xml、编程式注入不依赖) | 可选属性的注入 |
1.8 自动注入的注解对比
| 注解 | 注入方式 | 是否支持@Primary | 来源 | Bean不存在时的处理 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| @Autowired | 根据类型注入 | 是 | SpringFramework原生注解 | 可指定required=false来避免注入失败 |
| @Resource | 根据名称注入 | 是 | JSR250规范 | 容器中不存在指定Bean会抛出异常 |
| @Inject | 根据类型注入 | 是 | JSR330规范(需要导入jar包) | 容器中不存在指定Bean会抛出异常 |
@Qualifier:如果被标注的成员/方法在根据类型注入时发现有相同类型的Bean,就会根据该注解声明的name寻找对应的Bean
@Primary:如果有多个相同类型的Bean同时注册到IOC容器中,使用根据类型注入的注解时会注入标注的@Primarty注解的Bean
2.复杂类型的注入
- 数组
- List/Set
- Map
- Properties
2.1 创建复杂对象
创建一个Person类,里面定义比较复杂的属性

package com.feliks.spring.basic_di.g_complexfield.Bean;
import java.util.*;
public class Person {
private String[] names;
private List<String> tels;
private Set<Cat> cats;
private Map<String, Object> events;
private Properties props;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"names=" + Arrays.toString(names) +
", tels=" + tels +
", cats=" + cats +
", events=" + events +
", props=" + props +
'}';
}
public void setNames(String[] names) {
this.names = names;
}
public void setTels(List<String> tels) {
this.tels = tels;
}
public void setCats(Set<Cat> cats) {
this.cats = cats;
}
public void setEvents(Map<String, Object> events) {
this.events = events;
}
public void setProps(Properties props) {
this.props = props;
}
}2.2 xml复杂注入
xml中注册一个Person

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean class="com.feliks.spring.basic_di.g_complexfield.bean.Person"></bean>
</beans>2.2.1 数组注入
<bean>标签中,想要给属性赋值,全部都是用<property>标签,对于简单注入和Bean的注入,可以通过value和ref来完成,但是复杂类型就必须在标签体内写子标签了
来看看<prperty>标签下的子标签

使用数组的方式给Person注入值
<!-- 注册一个Person -->
<bean class="com.feliks.spring.basic_di.g_complexfield.bean.Person">
<property name="names">
<array>
<value>张三</value>
<value>李四</value>
</array>
</property>
</bean>2.2.2 List注入
<property name="tels">
<list>
<value>13222222222</value>
<value>13222221234</value>
</list>
</property>2.2.3 Set注入
提前声明好Cat的bean
<bean id="miao" class="com.feliks.spring.basic_di.g_complexfield.bean.Cat"/>在Person里使用Set注入猫猫
<property name="cats">
<set>
<bean class="com.feliks.spring.basic_di.g_complexfield.bean.Cat"/>
<ref bean="miao"/>
</set>
</property>


